
Background
Rastair is a command-line tool that allows the simultaneous detection of genetic variants and methylated positions from short-read sequencing data that was generated using a "mod-C→T" method, such as TAPS or Illumina's 5Base technology.
Traditional bisulfite sequencing (BS-seq) converts all non-modified cytosine (C) to thymine (T). This results in reads that differ substantially from the reference and are thus harder to align. Coverting most C to T also reduces the available information for variant identification. While several tools have been developed to overcome this problem, genetic variant calls from BS-seq remain substantially worse than those derived from whole-genome sequencing data.
In contrast, mod-C→T methods only affect around 60M positions in the human genome, equivalent to only approx. 2% of all nucleotides. This leads to greatly improved sequencing quality, higher mapping rates, and better yield from low-input DNA. It also makes it possible to identify genetic variation - in addition to epigenetic changes - with much higher accuracy. Rastair implements a fast and accurate algorithm to simultaneously provide such high-quality variant and methylation calls.
Latest Updates
Performance
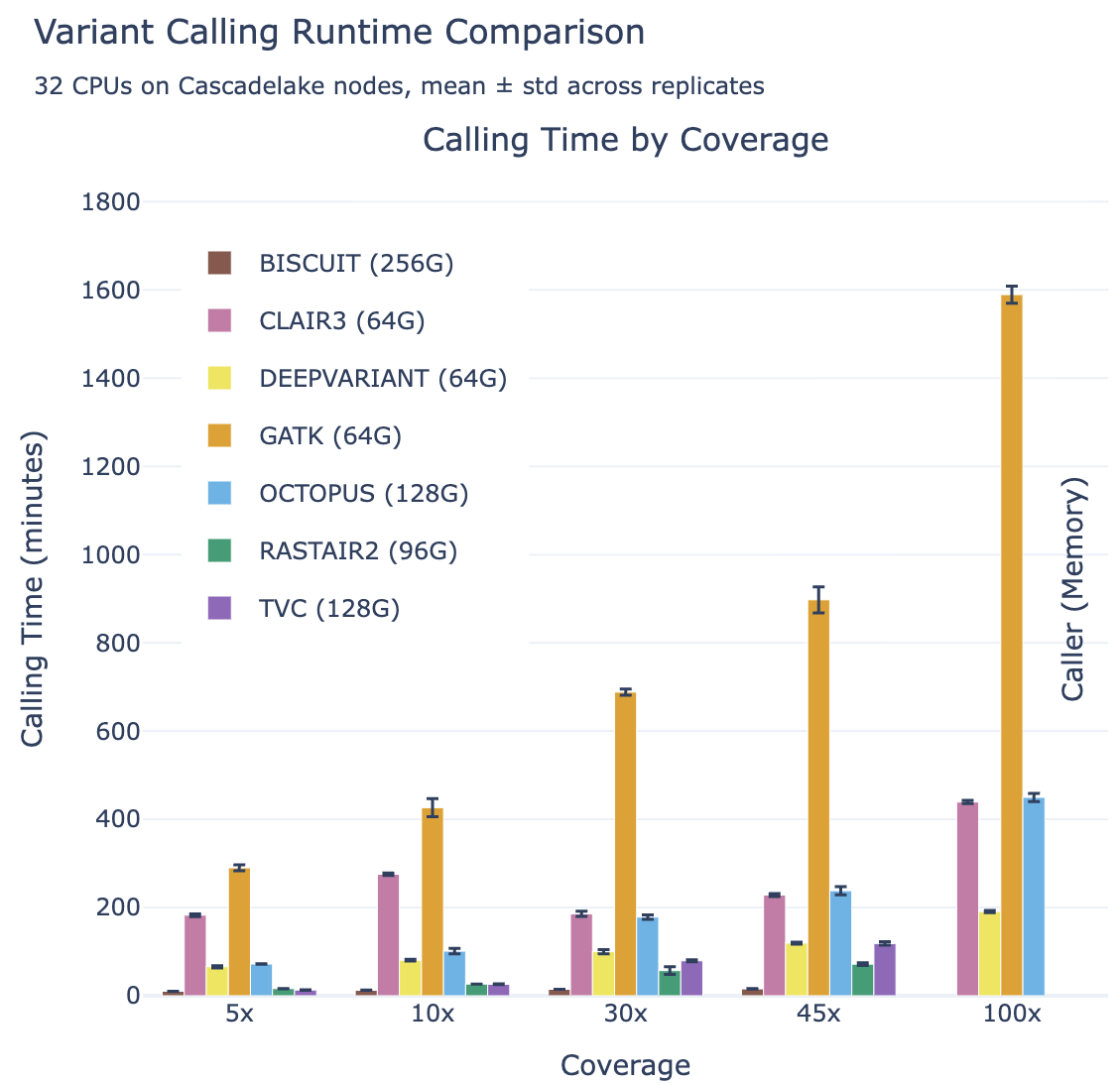
Rastair SNP calls on TAPS+ data
Rastair achieves similar variant-calling accuracy for SNP positions from TAPS+ and 5-Base data as state-of-the-art tools on "pure" whole-genome sequencing data, and significantly better than other tools built for TAPS+ or Bisulfite-seq data.
Meanwhile, rastair is significantly faster than other callers with comparable accuracy:
Rastair on 5-Base data
Rastair produces substantially fewer false-positives - at comparable sensitivity - than Illumina's DRAGEN 5-Base pipeline:
| Variant call overlap | Methylation overlap |
|---|---|
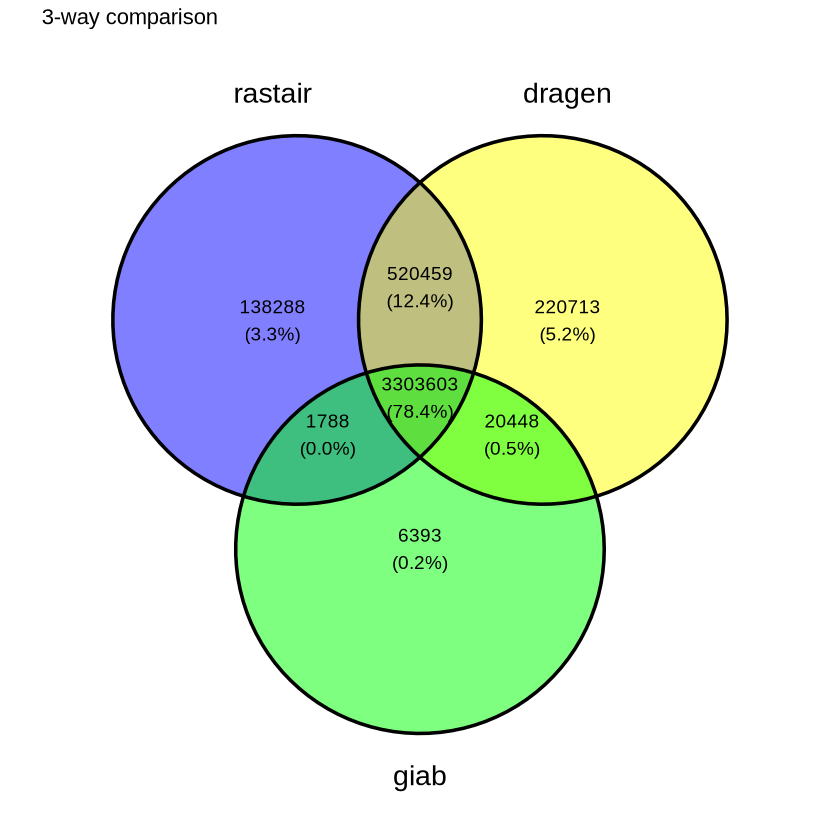 | 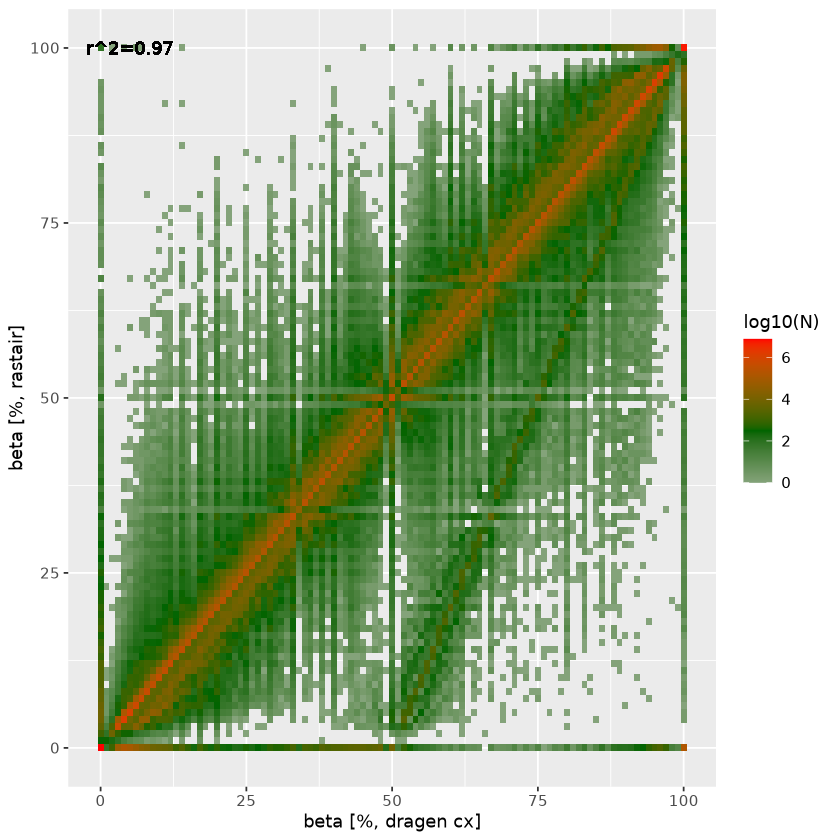 |
The Venn diagram on the left shows the overlap of SNPs called by rastair, Illumina's DRAGEN 5-Base pipeline, and the "Genome In A Bottle" truth set. Rastair produces fewer false positives, at the expense of slightly lower sensitivity. F1 Score DRAGEN: 0.899. F1 Score rastair: 0.906
On the right, we plot the agreement in estimated beta between rastair (y-axis) and DRAGEN (x-axis). The straight line off the diagonal with an intercept at DRAGEN beta=0.5 represent heterozygous C>T (and G>A) SNPs where Ts (and As) that are in fact genetic variants are incorrectly counted as methylation. Rastair corrects for this, thus lowering the estimated beta at those loci. There is also a subset of positions where dragen estimates full methylation (beta=1) where rastair estimates beta=0: these are homozygous C>T/G>A SNPs.
License
Rastair is free for academic and other non-commercial use, and the code is available on bitbucket. You can read the details of the license here.
For commercial entities that would like to use rastair beyond internal evaluation, please contact enquiries@innovation.ox.ac.uk quoting reference 24811.
Quick start
Installation
We provide pre-built binaries for Linux (x86), Mac (Apple Silicon) and Mac (Intel). We also provide a docker image. Conda integration is still work in progress, but will happen soon. For build instructions and more details, see the installation page.
Usage
Call methylation at all CpG positions (including CpGs formed by SNPs) from a bam file and output as a tabix-indexed bed file:
rastair call --bed output.bed.gz -r reference.fasta.gz input.bam
Rastair can also produce variant and methylation calls in VCF format:
rastair call --vcf output.vcf.gz -r reference.fasta.gz input.bam
For a more in-depth look at different use-cases of rastair with practical examples, see the examples section. For an explanation of the output file formats, see BED and VCF sections.
Get help
You can file an issue or question on our issue tracker over on bitbucket!
Citing rastair
A publication for rastair is in progress. We will update this page with a reference to the biorxiv preprint shortly.
Installation
Pre-built binaries
For convenience, we provide pre-built binaries for a number of platforms:
Linux
We provide a pre-built binary for Linux (x86):
- rastair-v2.0.0-x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu.tar.gz (64-bit, x86)
This binary was built on Ubuntu 20.04 but should work on most recent distributions.
While rastair itself is hard-linked and therefore independent of system libraries, this is unfortunately not yet the case for htslib. If your system uses a GLIBC older than 2.30, then you will have to compile from source.
Mac OSX
For Apple users, we provide both Apple Silicon and Intel binaries:
-
rastair-v2.0.0-aarch64-apple-darwin.zip (ARM "Apple Silicon", for all "M" line processors)
-
rastair-v2.0.0-x86_64-apple-darwin.zip (64-bit, older x86 Intel Macs)
Building from source
Pre-requisites
To compile from source, you need a working Rust installation (version 1.88 or later). Rastair depends on rust-htslib, which currently requires a working clang library as well as cmake. On most systems, these are either already available or can be installed using a standard package manager:
First, clone the repo:
git clone git@bitbucket.org:bsblabludwig/rastair.git
Then follow the platform-specific instructions below.
Ubuntu
sudo apt install libclang-dev cmake
Fedora
sudo dnf install -y clang cmake
Mac OSX (Homebrew)
We assume that you have Xcode developer tools installed. In that case, you only need
brew install cmake
Compile
Finally, build the project using:
cargo xtask release
The binary will be located in target/release/rastair.
On some systems, you might get performance improvements by allowing the compiler to use platform-specific optimisations:
RUSTFLAGS="-C target-cpu=native" cargo xtask release
Docker
You can install the pre-built docker image in the usual way:
docker pull sbludwig/rastair:version-2.0.0
Building using Docker
You can also build Rastair using Docker. Ensure you have Docker installed and running on your system, then, build the image:
docker build -t rastair .
This image is based on the R base image and includes all necessary dependencies to also run the bundled R scripts.
Conda
This is still work in progress: we hope to soon provide a bioconda recipe to install rastair.
Examples
rastair has two main modes:
- Call methylation per genomic position
- Annotate individual reads with the methylation states of the CpGs they contain
In addition, there are a number of convenience commands, e.g. to convert between different output file formats, and a small set of utility scripts written in R to produce quality-control metrics.
Below we will give some examples that cover common use-cases. You can find an in-depth documentation of the complete command line syntax here.
Nearly all rastair sub-commands are capable of multi-threading.
You can e.g. use -@ 4 to parallelise operations across 4 cores.
By default, rastair will try to use all available cores on your system.
1. Call genomic variants and methylated positions
By default, rastair will use a built-in ML model to classify variants as real or false.
If writing to a VCF (give a .vcf.gz file name) or BCF file (give a filename ending in .bcf),
all high-confidence calls will be included:
rastair call -r reference.fa.gz -o test.vcf.gz test.bam
You can restrict processing to only a specific genomic region. For example -l chr19 will process the entire chromosome 19.
You can also chose an interval within the chromosome: -l chr19:6103156-6143156.
Rastair will only report variants that pass its internal filters. If you want to report absolutely all candidate variants, regardless of their score, you can use the --all flag:
rastair call -r reference.fa.gz --all -o test.vcf.gz test.bam
Rastair will annotate variants with only a subset of all possible INFO and FORMAT tags. You can choose a custom set of annotations with e.g.
rastair call -r reference.fa.gz --vcf-info-fields AD,BQ,MQ,MQ0,ENT100,SC5,CPG,CPGnovo --vcf-format-fields GT,M5mC,ML -o test.bcf test.bam
You can find a description of all custom VCF fields used by rastair here.
rastair can produce uncompressed VCF, bgzip-compressed vcf.gz and bcf files. The format will be guessed from the file ending. If you want to stream output to STDOUT, you can do --vcf -
2. Only call methylation, do not report genetic variants (very fast)
BED output will only report CpG -- and de-novo CpG -- positions, which is a lot faster than processing all potential variants:
rastair call -r reference.fa.gz --bed test.bed.gz test.bam
Rastair will automatically produce bgzip compressed files if the output file name ends in .gz. They are also automaticall indexed with tabix for rapid access to specific genomic ranges:
tabix test.bed.gz chr19:6103156-6143156
This is usually orders of magnitude faster than using e.g. bedtools. You can also stream the bed file to STDOUT by setting --bed -.
In some cases, you might prefer to write the bed output to STDOUT and pipe it into another unix tool, e.g. to only report positions that are CpG in the references (ie exclude de-novo CpG):
rastair call -r reference.fa.gz --cpgs-only --bed - test.bam | grep -Fw REF
Ignore positions at the edges of reads
Sometimes, it might be desirable to ignore a certain number of bases at the beginning or end of a read when counting methylated positions.
This can e.g. account for loss of methylation due to sonication damage.
The command-line argument for this was inspired by MethylDackel.
However, we decided to only have one set of parameters: --nOT and --nOB.
Each of them takes a comma-separated list of 4 integers: [r1_5',r1_3',r2_5',r2_3'], denoting the number of bases from the start/end of read 1/2 that should be ignored.
Unlike MethylDackel, rastair's command line arguments always refer to the start/end position of the read in 5'→3' direction, not the position in the reference after alignment!
To give an example: imagine the following read pair
000000000111111111122
123456789012345678901
R1: CG--------TG--------->
R2: <AC-------------GC-
876543210987654321
111111111000000000
This "F1R2" read represents the OT (ie R1 is the OT, and R2 is the reverse complement of the OT).
A parameter of --nOT 0,5,0,5 will exclude the A at position 18 in R2, because it ocurrs within 5 bases from the end of R2 in read coordinates, not in reference coordinates.
3. Report methylation per-read
Many applications require information about the methylation of individual bases in each sequenced read. Rastair can report this information in bed format:
rastair per-read -r reference.fa.gz --bed test_per-read.bed.gz test.bam
For a description of the per-read bed format, see the BED format section.
The per-read output is also the input for your QC pipeline. For more details, read the qc section of this manual.
Command-Line Help for rastair
This document contains the help content for the rastair command-line program.
Version: 2.0.0
Command Overview:
rastair↴rastair call↴rastair per-read↴rastair convert↴rastair view↴rastair mbias↴rastair license↴
rastair
Rastair -- detect genetic variants and methylated positions from short-read sequencing data created using TET-Assisted Pyridine-Borane Sequencing.
See https://docs.rastair.com/ for more information.
Usage: rastair [OPTIONS] <COMMAND>
Subcommands:
call— Call methylated positionsper-read— Call methylation per-readconvert— Convert between different file formatsview— View internal format as JSON linesmbias— Calculate conversion per base position in readlicense— Show license -- rastair is licensed under a non-commercial use licence
Options:
-
-v,--verbose— Enable more loggingYou can also use the
RASTAIR_LOGenvironment variable to configure logging in a more precise way. See the documentation of thetracing-subscriberlibrary to learn more.
rastair call
Call methylated positions
Process TAPS-sequenced BAM files and call methylated positions.
If no output file is specified, the output is written to stdout. You can use --vcf and --bed to write to files instead.
If using -c (--cpgs-only), all CpG positions in the reference as well as de-novo CpGs are written. Stdout will default to BED.
Only variants that pass all filters are written by default. Use --all to get a full VCF file.
Usage: rastair call [OPTIONS] --fasta-file <FASTA_FILE> <BAM_FILE>
Arguments:
<BAM_FILE>— Path to sorted and indexed BAM file
Filter Options:
-
--keep-overlapping-reads— Whether to keep overlapping readsDefault value:
false -
--v-min-depth <V_MIN_DEPTH>Default value:
3 -
--max-coverage <MAX_COVERAGE>Default value:
1000 -
-q,--min-mapq <MIN_MAPQ>— Minimum mapping quality to consider a readDefault value:
1 -
-Q,--min-baseq <MIN_BASEQ>— Minimum base quality to consider a baseDefault value:
10 -
--nOT <N_OT>— For OT reads, exclude[r1_start, r1_end, r2_start, r2_end]bases from counting.The coordinates are relative to the read, so start is the distance from the 5' of the read, the end is the distance to the 3', irrespective of which way around the read aligns to the reference.
Also note that the distance is relative to read length, not alignment length, so soft-clipped bases count, too!
Default value:
0,0,0,0 -
--nOB <N_OB>— For OB reads, exclude[r1_start, r1_end, r2_start, r2_end]bases from counting.The coordinates are relative to the read, so start is the distance from the 5' of the read, the end is the distance to the 3', irrespective of which way around the read aligns to the reference.
Also note that the distance is relative to read length, not alignment length, so soft-clipped bases count, too!
Default value:
0,0,0,0 -
-f,--include-flags <INCLUDE_FLAGS>— Include reads that match all of these bit-flagsDefault value:
3 -
-F,--exclude-flags <EXCLUDE_FLAGS>— Exclude reads that match any of these bit-flagsDefault value:
3852 -
--cpg-novo-min-depth <CPG_NOVO_MIN_DEPTH>— Minimum reads needed in support of de-novo CpGDefault value:
2 -
--cpg-novo-min-baseq <CPG_NOVO_MIN_BASEQ>— Minimum base quality for de-novo CpGsDefault value:
15 -
--cpg-novo-min-mapq <CPG_NOVO_MIN_MAPQ>— Minimum mapping quality for de-novo CpGsDefault value:
50 -
--cpg-novo-min-vaf <CPG_NOVO_MIN_VAF>— Minimum variant allele frequency for de-novo CpGsDefault value:
0.2 -
--m-vaf-min <M_VAF_MIN>— The minimum variant allele frequencyDefault value:
0.2 -
--m-min-depth <M_MIN_DEPTH>— The minimum number of reads to call a position as methylatedDefault value:
3 -
--m-bq-ratio-min <M_BQ_RATIO_MIN>— The minimum quality ratio(ad_alt*bq_alt + 1) / (ad_ref*bq_ref + 1)Default value:
0.27 -
--m-read-position-min <M_READ_POSITION_MIN>— The minimum relative position in read for alt allele evidenceDefault value:
0.2 -
--m-read-position-max <M_READ_POSITION_MAX>— The maximum relative position in read for alt allele evidenceDefault value:
0.8 -
--m-max-coverage <M_MAX_COVERAGE>— The maximum coverage depth for methylation callingDefault value:
1000 -
--no-ml— Only use hard thresholds to call variants and methylation events.This disables using the machine learning models. This will make rastair much faster, but at the cost of accuracy.
-
--ml <ML>— Use machine learning model with this threshold value to call variants and methylation eventsWhen specified, a ML model will classify positions with a prediction score. Anything above this threshold is considered PASS.
For consistency with
--no-ml, this option can be also be specified as--mlwithout a value, which will use the default threshold.Default value:
0.50 -
--model <MODEL>— Path to the combined model file containing CpG, denovo, and others modelsDefault is the bundled model in the Rastair binary.
-
-c,--cpgs-only— Report CpGs only and default to BED outputOnly report positions that are CpGs in the reference or variants that would result in a de-novo CpG.
If combined with
--all, non-passing de-novo CpG positions and CpGs in the reference but without coverage in the sample will also be reported.Default value:
false -
--bed-include-empty— Include CpG positions with zero coverageThis can be useful to get a complete list of CpG positions in the output BED file. Note that this requires the input data to contain a complete list of CpG positions, e.g. by using the
--cpgs-onlyoption when calling methylation.
Input Options:
-r,--fasta-file <FASTA_FILE>— Path to sorted and indexed (via samtools faidx) FASTA file. Can be bgzip compressed, but requires both a gzi index and a fai index-l,--region <REGION>— Restrict to a specific chromosome or region of a chromosome. Format is "chr", "chr:start" or "chr:start-end", where start is 1-based and end is inclusive
Output Options:
-
--all— Output all positions, even if they do not pass filters.If combined with
--cpgs-only, only CpG positions will be reported, including non-passing de-novo CpGs, and those without coverage. -
-o,--vcf <VCF>— VCF/BCF output file path (use - to write to stdout)Format is guessed based on the file extension:
.vcffor VCF (uncompressed),.vcf.gzfor VCF (compressed),.bcffor BCF (compressed).mpk.lz4for internal format (Message Pack, LZ4-compressed) -
--vcf-info-fields <VCF_INFO_FIELDS>— Additional INFO fields to include in VCF output (comma-separated VCF field IDs)By default, only a minimal set is included.
Possible values:
AD,BQ,DP,MQ,MQ0,NS,AS_SB,SC5,AF,ABQ,AMQ,AS_SS_BQ,AS_SS_MQ,PIR,ENT100,NAB,NOI,M5mC_Strands,CPG,CPGnovo -
--vcf-format-fields <VCF_FORMAT_FIELDS>— Additional FORMAT fields to include in VCF output (comma-separated VCF field IDs)By default, only a minimal set is included.
Possible values:
GT,GL,GC,DP,M5mC,ML -
--bed <BED>— Output BED file with the called methylated positions -
--bed-format <BED_FORMAT>— Format of the output BED fileIf not specified, the format is guessed based on the file extension.
Possible values:
bed-gz: BGZIP compressed file, usually.bed.gzbed: Regular BED file, usually.bed
Processing Options:
-
--segment-max-length <SEGMENT_MAX_LENGTH>— Maximum length of a segment in basesUsed for splitting work between threads. Tweak this to adjust memory usage.
Default value:
100000 -
--segment-overlap <SEGMENT_OVERLAP>— Number of bases to overlap between segmentsHelpful to avoid missing variants at the edges of segments.
Default value:
200 -
--error-model <ERROR_MODEL>— The error model to useAccepts platform names or a custom error rate (e.g., 0.005)
Default value:
novaseq6000Possible values:
miseq: MiSeq https://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_instruments/miseq.htmlminiseq: MiniSeq https://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_instruments/miniseq.htmlnextseq500: NextSeq500 https://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_instruments/nextseq-500.htmlnextseq550: NextSeq550 https://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_instruments/nextseq-550.htmlhiseq2500: HiSeq2500 https://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_instruments/hiseq_2500.htmlnovaseq6000: NovaSeq6000 https://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_instruments/novaseq-6000.htmlhiseqxten: HiSeq X Ten https://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_instruments/hiseq-x.html
-
--vcf-threads <VCF_THREADS>— Number of threads to use for writing (and compressing) VCF filesThis is subtracted from
--threadsbut never below 1. Adjust this if you think that VCF writing is a bottleneck, e.g. when the output files contain a lot of positions.Default value:
1 -
-@,--threads <TOTAL_THREADS>— Number of threads to use for processing the BAM file. Will use all available threads when not specified.Note that VCF writing might use additional threads internally for compression. This can be overwritten with
--vcf-threads.Default value:
10[env:RASTAIR_THREADS]
rastair per-read
Call methylation per-read
This will produce a bed file that list the methylation status of all CpGs in every read that overlaps a CpG, plus some other metadata
Usage: rastair per-read [OPTIONS] --fasta-file <FASTA_FILE> <BAM_FILE>
Arguments:
<BAM_FILE>— Path to sorted and indexed BAM file
Filter Options:
-
-f,--include-flags <INCLUDE_FLAGS>— Include reads that match all of these bit-flagsDefault value:
3 -
-F,--exclude-flags <EXCLUDE_FLAGS>— Exclude reads that match any of these bit-flagsDefault value:
3852 -
-w,--max-read-length <MAX_READ_LENGTH>— expected maximum read length. If set too short, some read positions might not get counted. Safest to set this a bit higher than the actual read length, to allow for indels in readsDefault value:
200 -
-q,--min-mapq <MIN_MAPQ>— Minimum mapping quality per aligned readDefault value:
1 -
--exclude-ambiguous— Exclude reads where the orientation cannot be unambiguously determined -
--count-clipped— Count clipped positionsBy default, rastair ignores the leading (soft and hard) clipped positions in the "positions in read" columns. The indices written can be seen as "position in read relative to the first base actually aligned".
If
--count-clippedis set, clipped positions will instead be counted. The indices written then match the sequence of the read.
Input Options:
-r,--fasta-file <FASTA_FILE>— Path to sorted and indexed (via samtools faidx) FASTA file. Can be bgzip compressed, but requires both a gzi index and a fai index-l,--region <REGION>— Restrict to a specific chromosome or region of a chromosome. Format is "chr", "chr:start" or "chr:start-end", where start is 1-based and end is inclusive--calls <CALLS>— BED file Rastair wrote with methylation calls per position
Output Options:
-
-A,--all-reads— Report reads with no CpGs in them -
--bed <BED>— Output BED file with all readsDefault value:
- -
--bed-format <BED_FORMAT>— Format of the output BED reads fileIf not specified, the format is guessed based on the file extension.
Possible values:
bed-gz: BGZIP compressed file, usually.bed.gzbed: Regular BED file, usually.bed
Processing Options:
-
--segment-max-length <SEGMENT_MAX_LENGTH>— Maximum length of a segment in basesUsed for splitting work between threads. Tweak this to adjust memory usage.
Default value:
100000 -
--segment-overlap <SEGMENT_OVERLAP>— Number of bases to overlap between segmentsHelpful to avoid missing variants at the edges of segments.
Default value:
500 -
-@,--threads <TOTAL_THREADS>— Number of threads to use for processing the BAM file. Will use all available threads when not specified.Note that VCF writing might use additional threads internally for compression. This can be overwritten with
--vcf-threads.Default value:
10
rastair convert
Convert between different file formats
Usage: rastair convert [OPTIONS]
Filter Options:
-
-c,--cpgs-only— Report CpGs only and default to BED outputOnly report positions that are CpGs in the reference or variants that would result in a de-novo CpG.
If combined with
--all, non-passing de-novo CpG positions and CpGs in the reference but without coverage in the sample will also be reported.Default value:
false -
--bed-include-empty— Include CpG positions with zero coverageThis can be useful to get a complete list of CpG positions in the output BED file. Note that this requires the input data to contain a complete list of CpG positions, e.g. by using the
--cpgs-onlyoption when calling methylation. -
--bed-ml <ML_THRESHOLD>— Minimum ML score to consider a position as variantThis does nothing if the input data does not contain ML scores.
Default value:
0.50
Input Options:
-
-i,--input <INPUT>— Input fileDefault value:
- -
-f,--input-format <INPUT_FORMAT>— Input file format, guessed from file extension if not specifiedPossible values:
vcf: Text-based VCF format (.vcf)bcf: Binary VCF format (.bcf)vcf-compressed: Compressed text-based VCF format (.vcf.gz)mpk.lz4
Output Options:
-
-o,--output <OUTPUT>— Output fileDefault value:
- -
-F,--output-format <OUTPUT_FORMAT>— Output file format, guessed from file extension if not specifiedPossible values:
vcf: Text-based VCF format (.vcf)bcf: Binary VCF format (.bcf)vcf-compressed: Compressed text-based VCF format (.vcf.gz)mpk.lz4bed: Regular BED file, usually.bedbed-gz: BGZIP compressed file, usually.bed.gz
-
--all— Output all positions, even if they do not pass filters.If combined with
--cpgs-only, only CpG positions will be reported, including non-passing de-novo CpGs, and those without coverage.
Processing Options:
-
--error-model <ERROR_MODEL>Default value:
novaseq6000Possible values:
miseq: MiSeq https://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_instruments/miseq.htmlminiseq: MiniSeq https://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_instruments/miniseq.htmlnextseq500: NextSeq500 https://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_instruments/nextseq-500.htmlnextseq550: NextSeq550 https://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_instruments/nextseq-550.htmlhiseq2500: HiSeq2500 https://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_instruments/hiseq_2500.htmlnovaseq6000: NovaSeq6000 https://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_instruments/novaseq-6000.htmlhiseqxten: HiSeq X Ten https://support.illumina.com/sequencing/sequencing_instruments/hiseq-x.html
rastair view
View internal format as JSON lines
Usage: rastair view [OPTIONS] <INPUT>
Arguments:
<INPUT>— Message Pack file to view
Output Options:
-
-o,--output <OUTPUT>— Message Pack file to viewDefault value:
-
rastair mbias
Calculate conversion per base position in read
This will produce a mbias.html file with information about conversion counts relative to read position.
Please note that this is currently implemented as an R script. Unless you're using the official Docker image, you need to install R and the necessary packages yourself.
Usage: rastair mbias [OPTIONS] <BED_FILE>
Arguments:
<BED_FILE>— Input per-read BED file (can be gzipped)
Filter Options:
-
--region <REGION>— Genomic region -
--include-flag <INCLUDE_FLAG>— Include bitflag as integerDefault value:
3 -
--exclude-flag <EXCLUDE_FLAG>— Exclude bitflag as integerDefault value:
3852 -
--read-length <READ_LENGTH>— Read length as integer
Options:
-
--r-script-dir <R_SCRIPT_DIR>— Override directory to find R scriptsWhen not set, tries to look for
$rastair_path/scriptsand./scripts[env:R_SCRIPT_DIR]
Output Options:
-
--output-prefix <OUTPUT_PREFIX>— Output path prefixDefault value:
.
Processing Options:
-
--tabix-path <TABIX_PATH>— Path to tabix executableDefault value:
tabix
rastair license
Show license -- rastair is licensed under a non-commercial use licence
Usage: rastair license
This document was generated automatically by
clap-markdown.
Quality control report
Rastair comes with a helper script, written in R, which generates a comprehense QC report for your library.
If not using the docker image: The QC tool requires a working installation of R with RMarkdown, data.table, ggplot2 and argparser libraries. You can install all of them at once with
install.packages(c("argparser", "data.table", "ggplot2", "rmarkdown"))
Generating QC reports
To generate the report, you need to first generate per-read bed output as described in the examples section.
You can speed this up by e.g. restricting to a smaller chromosome with e.g. -l chr17 as an additional argument to rastair per-read.
Once you have your per-read output, you generate the html report with
mkdir -p test_qc
rastair mbias --output-prefix test_qc test_per-read.bed.gz
This will produce a file called mbias.html in the test_qc directory.
Elements of the QC report
Conversion of methyl-C to T should be independent of where in a sequencing read the methylation ocurred. However, in reality, a number of experimental procedures can affect the evenness of conversion. For example, sonication or enzymatic digestion of genomic DNA can produce single-stranded ends. When these are repaired for A-tailing, the newly synthesized parts will be unmethylated.
To identify any potential issues in your data, we are providing two types of plots to investigate the evenness of methylation:
M-bias
The classic "methylation bias" (aka M-bias) plot shows the average methylation per position in a read:
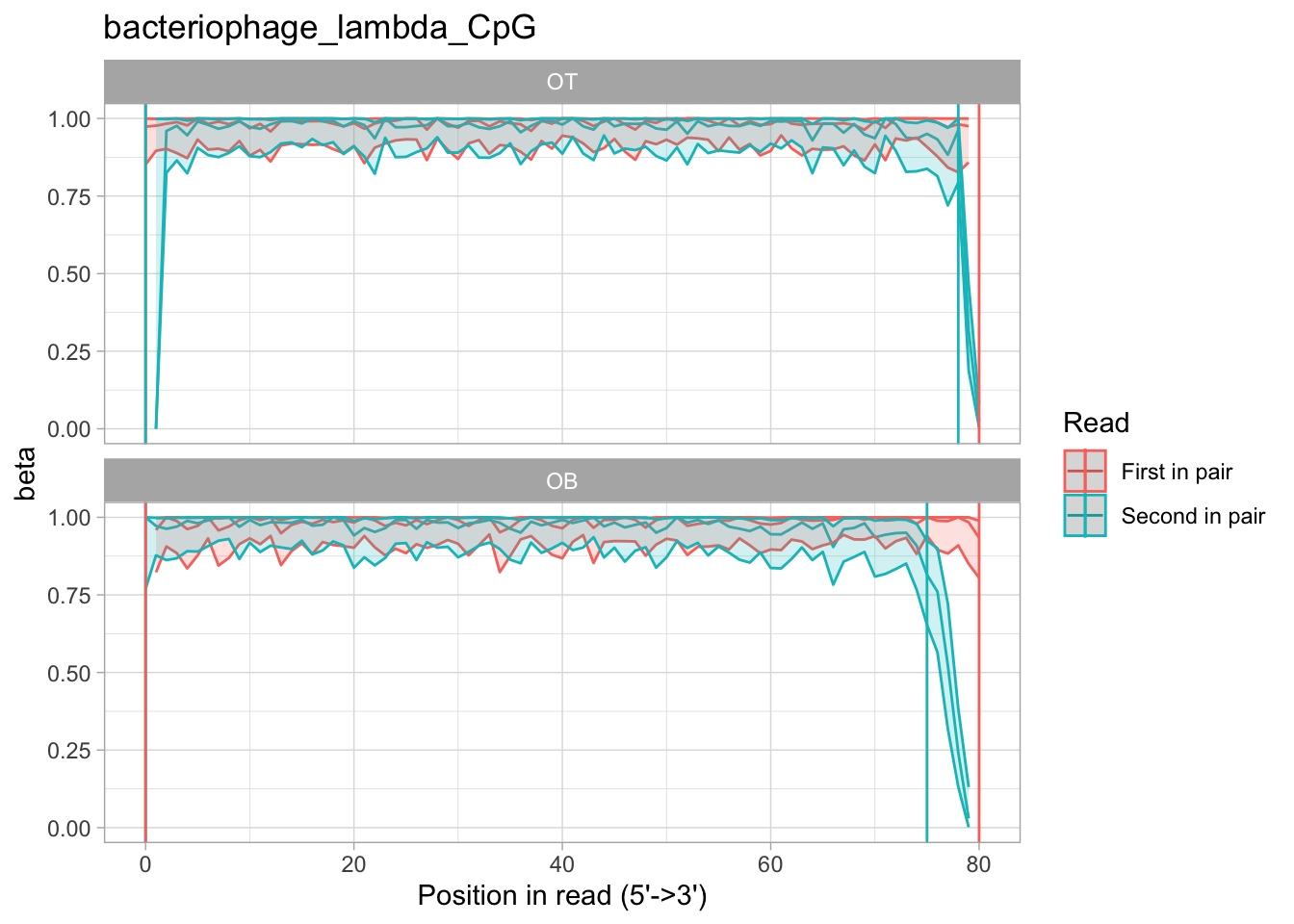
We distinguish between OT and OB fragments, and show average methylation for R1 and R2 reads separately. This is an example of an enzymatically fully methylated piece of DNA that we use as a control, so methylation is nearly 100% across most reads. However, you can see that the ends of R2 of OB fragments seem to have lost methylation information. This could be corrected with the --nOT and --nOB arguments to rastair call.
To facilitate choosing the right cutoff parameters, we also generate a text file for each processed chromosome that contain the estimated optimal --nOT and --nOB settings, respectively.
In this example, the script produced this:
cat bacteriophage_lambda_CpG_cutoffs.txt
0,0,0,2
0,0,0,5
In other word, it suggested we set --nOT 0,0,0,2 and --nOB 0,0,0,5, ie remove the last 2 and 5 bases of R2 in OT and OB, respectively.
V-bias
In some cases, for example when DNA is enzymatically digested in vivo or in vitro, there might be a wide range of fragment sizes. We have observed in some instances that fragment size has an impact on methylation bias per read position. To visualise this, we provide what we call a "V-bias" plot:
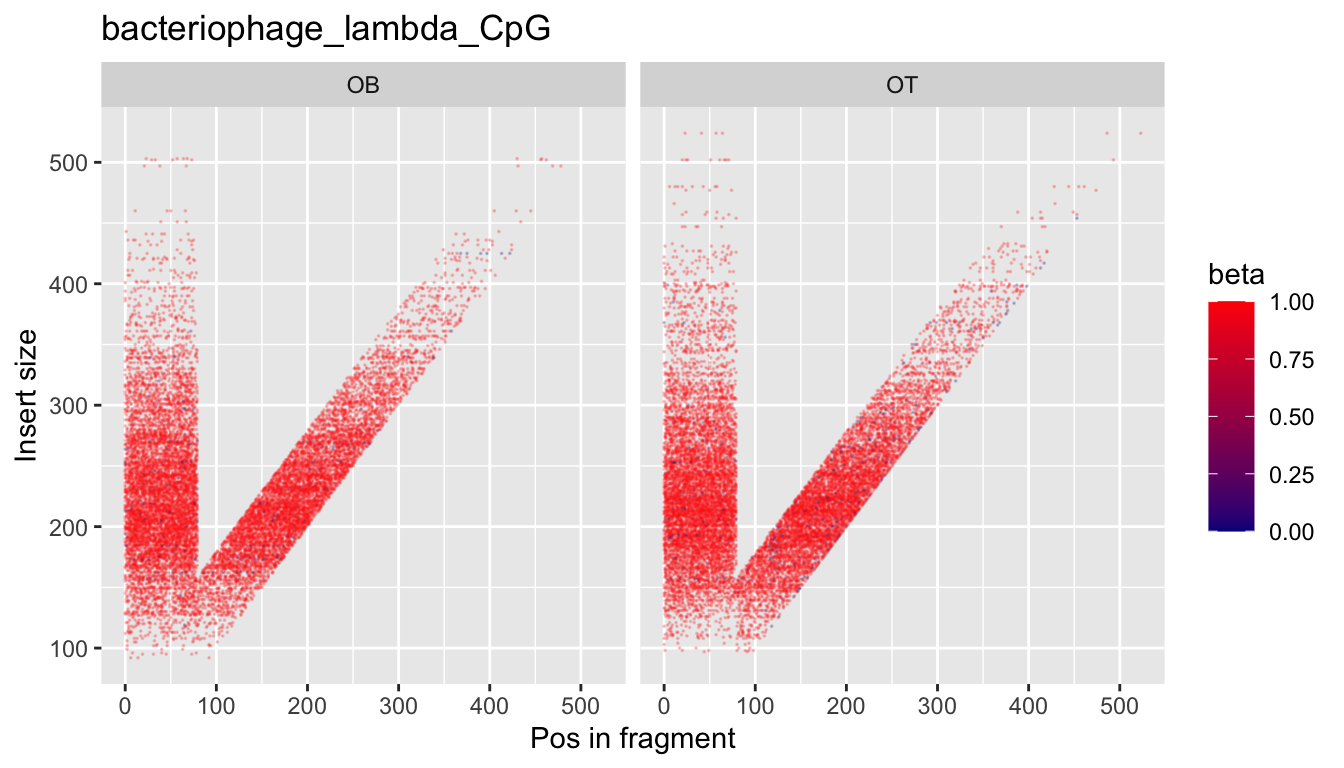
Here, colour denotes methylation, while the y-axis reflects the length of the original fragment, assuming paired-end sequencing.
De-novo CpGs
In addition to looking at methylation of known CpG sites,
i.e. sites that are already present in the reference genome,
Rastair can also call de-novo CpG sites.
These are sites where a C and/or G alternative allele exists in reads
followed/preceded by a G and/or C reference allele,
and thus creating new CpG sites.
Example
Here is an example of a de-novo CpG site in a pileup:
Position 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Reference: A T C C T A G C Strand
Reads: A T T G T A G C +
A T C A T A G C -
A T C A T A G C -
A T T G T A G C +
A T T G T A G C +
↑
De-novo CpG created by C>G variant
In this example, some reads have a G at position 3 where the reference has a C.
This creates a new CpG dinucleotide (CG) that is not present in the reference genome.
This newly generated CpG is methylated, which means that both the C and the G position
will show T/A at OT/OB reads, respectively!
Methylation of de-novo CpGs
After Rastair has identified de-novo CpG sites,
it will also call methylation for these sites.
For a methylated de-novo CpG site,
there have to be both C and T (or G and A) alternative alleles,
which means the amount of evidence present is generally lower than for known CpG sites.
The same filter criteria as for known CpG sites are applied.
Methylation calling in Rastair
A core feature of Rastair is the ability to call methylation from TAPS sequencing data.
In TAPS sequences, a mehtylated position is a CG sequence
where the OT C is read as T and the OB G is read as A.
For example, given this reference and pileup (. means reference base):
Ref A T C G C C T Strand
Reads . . . . . . . +
. . . A . . -
. . . A . . . -
. . T . . . . +
. . . . . . . -
. . T . . . . +
. . T . . . . +
We can see that in the CG context, the C is read as T in 3 OT reads, and the G is read as A in 2 OB reads.
This gives us a good indication that the C is methylated.
Output (VCF)
When methylation calling is enabled, Rastair will include all CpG sites in the output VCF file.
It will set the beta value(s) in the M5mC format field for each site.
In most cases, a single beta value is reported. However, when a position is both:
- Part of an original CpG site in the reference genome, AND
- Affected by a variant that creates a de-novo CpG site
Then two beta values will be reported in the M5mC field:
- The first value represents the methylation level of the original CpG context
- The second value represents the methylation level of the de-novo CpG context
This allows for accurate methylation quantification in complex scenarios where multiple CpG contexts overlap at a single position.
If a certain threshold of confidence is met,
the alt allele will be set to . since it is not considered a variant in the traditional sense.
Criteria for methylation calling
- Only CpG sites (including de-novo CpGs) are considered for methylation calling.
- OT reads with
Ton the refCposition - OB reads with
Aon the refGposition - Not a homozygous variant away from C/T
- Sufficient read depth (controlled with
--v-min-depth) - High base quality (controlled with
--min-baseq) - High mapping quality (controlled with
--min-mapq)
Beta value correction
When a CpG also overlaps a heterozygous variant, then only the non-variant C/G bases are available for methylation. Where the variant allele is a T/A at a C/G position, respectively, this thus requires that we do not count the "genetic T/A alleles", but only the chemically converted T/A. Unfortunately, we do not know which ones are which, so rastair currently uses a simple heuristic: we assume a diploid genome, and thus half of all reads are expected to derive from the T/A allele, while the other half represents the C/G. We therefore only consider the excess of T/A reads beyond half the reads observed as bona-fide "modified":
Where are the number of modified reads and are the number of unmodified reads.
Machine Learning Models
Rastair uses ML to distinguish true methylation calls and variants from sequencing artifacts (and noise). The ML models evaluate each alt at each position and assign a prediction score for that alt to be a true variant.
By default, ML is enabled with a threshold of 0.5.
A pre-trained model is bundled with Rastair.
The model handles three contexts with distinct sub-models:
- CpG methylation sites: Standard 5mC detection in CpG sites
- De-novo CpG: New methylation sites not in reference
- Other variants: Non-CpG SNPs and indels
Some features are shared across models, but some are model specific. Here is a plot of all features used in each model, ranked by importance:
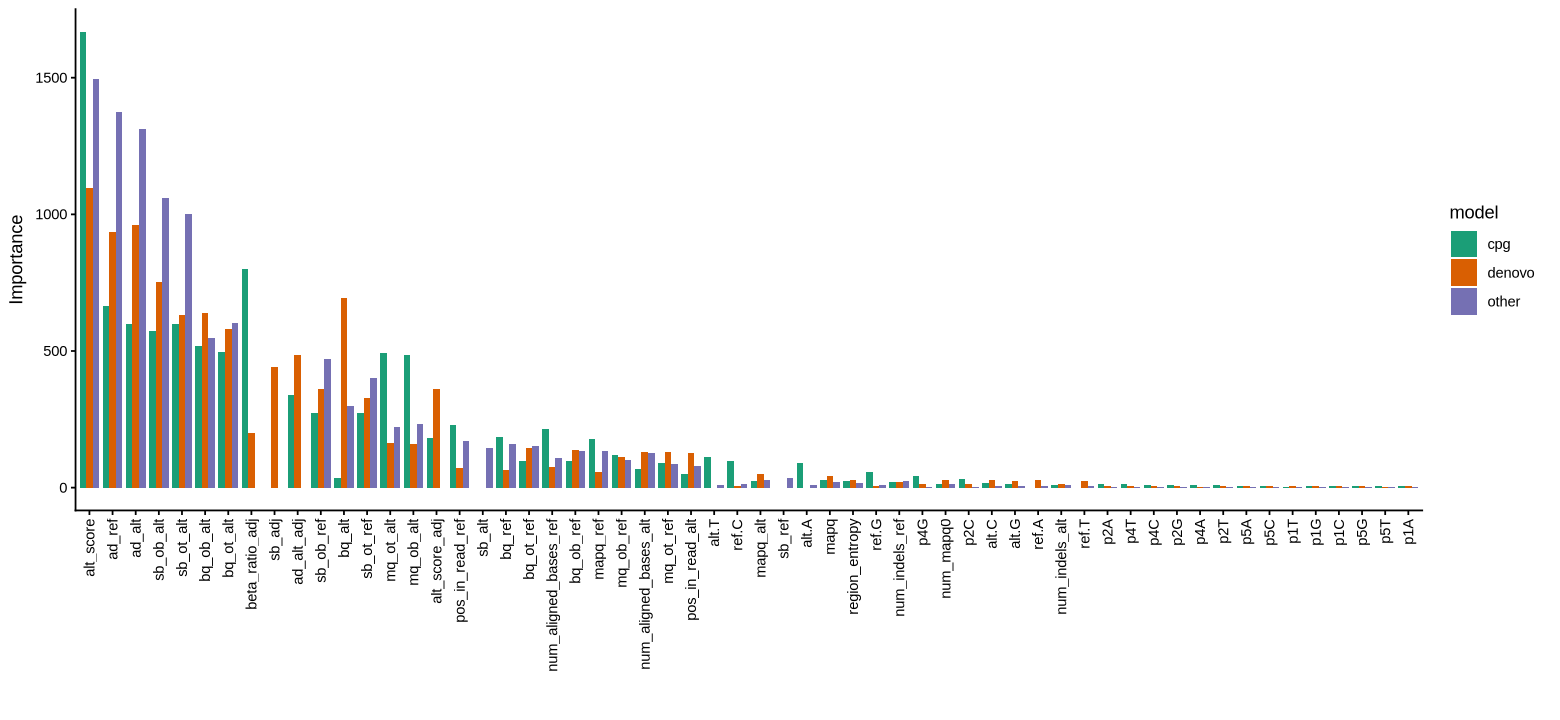
Here, _adj refers to a feature of the adjacent nucleotide, ie the C when evaluating a G or the G when evaluating a C. All scores that refer to allele counts are normalised either implicitly (where the score itself is a ratio) or explicitly to the total depth at that position. Of note, the alt_score is a simple ratiometric score to establish the base-quality weighted enrichment of variant reads over non-variant reads: , where refers to the number of reads with ref/alt on the OT (for C positions) or OB (for G positions), and is the corresponding strand-specific RMS of base qualities.
The resulting ML scores are calibrated using Platt scaling, which normalizes score distributions across the three separate sub-models.
Adjusting the Threshold
After calibration, a threshold of should filter out all candidate variants with less than 50% likelihood of being true. Empirically, we determined this to be a good compromise between sensitivity and specificity. However, you can manually override this:
rastair call --ml 0.7 input.bam
Values above 0.5 will shift the balance towards higher specificity at the expense of sensitivity.
If you care primarily about speed but do not need strict variant calling, e.g. when you only want to call methylation at known CpGs, you can turn the ML scoring off:
rastair call --no-ml input.bam
There are a range of hard-threshold filters that can be customized with different command line arguments. Refer to the cli documentation for details.
Genotyping
Rastair uses ML scores to determine which alternative alleles represent true genetic variants, then applies statistical methods to estimate zygosity. Rastair only support diploid genotyping (two chromosome copies) at this time.
Multi-Allelic Sites
When multiple alternate alleles are present at the same genomic position, they are combined into a single VCF record with comma-separated ALT values.
For example, with REF=A and ALT=T,G, the genotype represents the complete set of observed alleles:
- A genotype of
1/2means "on one chromosome there was a T (allele 1), on the other was a G (allele 2)" - A genotype of
0/1means "on one chromosome there was the reference A (allele 0), on the other was a T (allele 1)" (G alt did not pass filters) - A genotype of
1/1means "both chromosomes had a T (allele 1)" (only T alt passed filters)
This representation follows VCF specification standards where allele indices start at 0 for the reference, and 1, 2, 3... for the alternate alleles in order.
Genotype Calls
- Homozygous Reference (
0/0): no alternate alleles passed filters - Heterozygous (
0/1): One alternate allele passed filters but read counts show a mix of reference and alternate reads - Homozygous Alternate (
1/1): an alternate allele passed filters and read counts show predominantly alternate reads, consistent with two copies of the variant - Compound Heterozygous (
1/2,2/3, etc.): Multiple alternates passed filters and read counts support different variants on each chromosome copy
Confidence Scoring
Confidence values reflect call certainty:
- For
0/0calls: based on the margin between the ML threshold and the highest-scoring alternate - For variant calls: based on how well read count ratios match the expected distribution
Biological Interpretation
A genotype represents the complete set of observed alleles in an individual. All alternate alleles listed in a VCF record's ALT field are simultaneously present at that position in at least one chromosome copy. In most cases:
- If only one variant passes filters, the genotype indicates whether it's present on one chromosome copy (heterozygous
0/1) or both copies (homozygous alternate1/1) - If multiple variants pass filters, they represent compound heterozygosity where different variants are present on different chromosome copies (e.g.,
1/2)
Strand-Specific Counting
For C→T and G→A variants, only one strand is used to avoid confounding with methylation.
For all other variant types, both strands contribute to genotyping.
VCF
The main output of Rastair is a VCF file. It contains all metrics that Rastair calculates, either for all variants, or only for CpG sites.
BCF output, compression
VCF files are text-based and can be quite large, especially for whole-genome sequencing data.
Rastair can also output BCF files (binary VCF format) which are more compact and faster to read.
Alternatively, it can compress the VCF file transparently using bgzip.
All formats can be read by bcftools, just like regular VCF files.
By specifying the file extension (.vcf, .bcf, or .vcf.gz) Rastair will automatically detect which format to write.
Fields
By default, only a few fields are include.
You can enable more using the --vcf-info-fields and --vcf-info-fields flags with comma-separated field names.
See VCF Fields for a detailed description of the fields in the VCF output.
Methylation information
The estimated value is encoded in the VCF file through the M5mC FORMAT field which is provided at all positions where CPG or CPGnovo are set. We include all CpG positions in the reference, whether they overlap a variant or not. Where they do not overlap a variant, the ALT is set to ., aka the missing value.
While rare, it is possible to have more than one methylation call at one position. This can occur in CCG positions where the middle C is also a C>G SNP. This leads to two alleles, one where the middle position is a G and the other where it is a C. Each could be methylated at different levels. In these cases, the M5mC value will be a comma-separated list.
Quality scores
Quality scores in the vcf output reflect the ML-derived probability that a variant is "true". When we train the ML model, we calibrate it against a validation dataset and estimate the fraction of true SNPs called at every score cutoff. Based on this, we can fit a regression ("Platt scaling") that converts the score into a probability that a SNP call is true. For the quality score, we encode the inverse as Phred: . For methylated positions where no variants were observed, we record the maximum Phred, ie. 99.
VCF Fields
Rastair's output follows the VCFv4.5 specification.
Filters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
PASS | All filters pass |
lowDp | Low read depth |
dnCpG_lowDp | Low read depth for de-novo CpG candidate |
dnCpG_bq | Low base quality for de-novo CpG candidate |
dnCpG_mapq | Low mapping quality for de-novo CpG candidate |
dnCpG_vaf | Low variant allele frequency for de-novo CpG candidate |
dnCpG_adj | Included as adjacent position for de-novo CpG candidate, but other position did not pass filters |
m_vaf | Low variant allele frequency for methylation candidate |
m_bq_ratio | Low quality ratio for methylation candidate |
m_pos | Alt allele evidence from read edges for methylation candidate |
m_highDp | Excessive coverage for methylation candidate |
pre_ml | Low amount of usable evidence, skipping ML |
low_ml_score | Machine Learning module prediction below threshold |
Info Fields
| Name | Description | VCF Type | Rust Type | Occurance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
AD | Total read depth for each allele | Integer | usize | R |
BQ | RMS base quality | Float | RootMeanSquare | 1 |
DP | Combined depth across samples | Integer | usize | 1 |
MQ | RMS mapping quality | Float | RootMeanSquare | 1 |
MQ0 | Number of MAPQ == 0 reads | Integer | usize | 1 |
NS | Number of samples with data | Integer | usize | 1 |
AS_SB_OT | OT counts per allele | Integer | u32 | R |
AS_SB_OB | OB counts per allele | Integer | u32 | R |
SC5 | 5-base sequence context centered on the variant position | String | SmolStr | 1 |
AF | Allele frequency for each ALT allele in the same order as listed (estimated from primary data, not called genotypes) | Float | f64 | A |
ABQ | RMS Base quality per allele | Float | f64 | R |
AMQ | RMS Map quality per allele | Float | f64 | R |
AS_SS_BQ_OT | Strand-specific RMS of base quality per allele on the original top strand | Float | f32 | R |
AS_SS_BQ_OB | Strand-specific RMS of base quality per allele on the original bottom strand | Float | f32 | R |
AS_SS_MQ_OT | Strand-specific RMS of mapping quality per allele on the original top strand | Float | f32 | R |
AS_SS_MQ_OB | Strand-specific RMS of mapping quality per allele on the original bottom strand | Float | f32 | R |
PIR | RMS of relative position in read | Float | f64 | R |
ENT100 | Shannon entropy of 100bp sequence context around variant position. Value range (0..2) | Float | f64 | 1 |
NAB | RMS of number of aligned bases | Float | f64 | R |
NOI | RMS of number of indels | Float | f64 | R |
M5mC_Strands | Number of reads that are evidence for unmodified, modified, no SNP, snp | Integer | u32 | 4 |
CPG | Is this a CpG site? | Flag | bool | 0 |
CPGnovo | De-novo CPG candidate: Could the alt alleles create a new CpG site? | Flag | bool | 0 |
Format Fields
| Name | Description | VCF Type | Rust Type | Occurance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
GT | Genotype | String | GenotypeAllele | 1 |
GL | Genotype likelihoods, Phred-scaled | Integer | Phred> | G |
GC | Genotype confidence, Phred-scaled | Integer | Phred> | G |
DP | Read depth | Integer | usize | 1 |
M5mC | Methylation level at CpG sites | Float | Option<f64> | M |
ML | Prediction of methylation/variant likelihood by rastair's machine learning model | Float | f64 | A |
BED Format
Rastair can output BED files of two different kinds:
- CpG sites:
A file containing all CpG sites with their methylation status.
Generated using the
callcommand and specifying--bed(or usingconvert). - Per-read methylation:
A file containing the methylation status of each CpG site for each read.
Generated using the
per-readcommand.
CpG Sites
The BED file for CpG sites contains the following columns:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
chrom | Chromosome name |
start | Start position of the CpG site (0-based) |
end | End position of the CpG site (1-based) |
name | Name of the CpG site (e.g., "CpG1") |
beta_est | Estimated beta value for methylation (empty string if not present) |
strand | Strand information (e.g., "+", "-") |
unmod | Number of unmethylated reads |
mod | Number of methylated reads |
no_snp | Number of reads not counting as SNPs |
snp | Number of reads counting as SNPs |
coverage | Total coverage at the CpG site |
genotype | C/C, C/T, G/G, G/A, T/T, or A/A |
gt_p_score | P-value for the genotype call |
gt_conf_score | Confidence score for the genotype call |
cpg | REF if CpG site occurs in reference genome, NEW if it is a de-novo CpG site |
Per-Read Methylation
The BED file for per-read methylation contains the following columns:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
chr | Chromosome name |
start | Start position |
end | End position |
read_id | Name of read |
mapq | Mapq of read |
orientation | Orientation of read, either + or - |
insert_size | Absolute fragment length (non-directional) |
read_length | Read length |
flag | Flag of read (decimal, same as in BAM) |
num_cpg | Number of CpGs in a read |
num_mod | Number of modified CpGs |
mod_cpgs | Positions in read of modified CpGs |
unmod_cpgs | Positions in read of unmodified CpGs |
snp_cpgs | Positions in read that are SNPs (mutated) |
mod_denovos | Positions in read of de-novo CpG that are mutated |
unmod_denovos | Positions in read of de-novo CpG that are mutated |
Note: The positions in reads take indels into account,
meaning that the positions are relative to the read, not the reference genome.
If --count-clipped is set, it will also include leading clipped bases.
modBAM
The modBAM format is a BAM/SAM file
that contains modified base information in the MM and ML tags
as specified by the Optional Fields Specification.
This format is useful for storing per-read modification information alongside the alignment data.
In Rastair, we're mainly interested in storing CpG methylation information, which is represented
as 5-methylcytosine (5mC) on the C and G on the opposite strand.
Change of read sequence
The read sequence in the modBAM file will differ from the read sequence in the input BAM file.
Since Rastair deals with reads from TAPS,
methylated Cs are represented as Ts in the read sequence.
However, both the MM tag specification and other tools like modkit
expect the fundamental base to be in the read sequence.
That means, for a methylated CpG,
the read sequence should contain a C on the forward strand and a G on the reverse strand,
with only the MM tag indicating the modification
instead of the presence of a T or A in the sequence.
To be compatible with this, Rastair will rewrite the read sequence at methylated positions when writing the modBAM output.
Format converter
Rastair includes a convert subcommand
that allows converting between many of the supported file formats.
Streaming
Rastair's convert command supports streaming input and output,
so that it can be used in a pipeline with other commands.
Since it only guesses the formats based on file names,
they need to be specified explicitly when streaming.
For example, to convert the first entries from a VCF file to BED format you can use the following command:
head -n1000 test.vcf | rastair convert -f vcf -F bed | less
Possible conversions
Note that not all formats contain the same information. Rastair can only convert to formats that contain the same or less information than the source.
That means, for a given input, it can convert to a format in the same group or a lower group in this list:
-
Internal format (
.mpk.lz4)Rastair's internal data structures, serialized. Contains all metrics in their original structure. Not guaranteed to be stable across versions.
-
Contains basically all information, serialized in a standard way. Can be processed using BCFtools.
-
BED (
.bed) and per-read BED (.reads.bed)Contains the most important calling information. Can be processed using BEDtools (or anything else that can read tab-separated-values files).
Rastair Architecture
Rastair performs simultaneous variant and methylation calling from TAPS sequencing data. This section describes three key architectural components that enable the robust and performant genome-wide analysis.
Parallel Pipelined Iterator
Rastair processes genomic data through a parallel architecture that maintains positional context while achieving efficient CPU utilization at low memory usage (~250MB per worker thread).
Segmentation: The genome is divided into overlapping segments (typically 1-10 Mb). Each segment has a "core" region flanked by "overlap" regions. This design ensures that positions at segment boundaries have access to adjacent positions needed for CpG pair analysis and de-novo CpG detection. After processing, only core positions are emitted, preventing duplicates.
Thread-Local Readers: Each worker thread maintains its own BAM and FASTQ file handles, avoiding lock contention and serialize I/O. Using index files (FAI, CSI, or TBI) enables efficient parallel random access.
Ordered Channel: An ordered channel buffers worker results and reorders them by segment index before forwarding to the writer thread. A buffer size of 10 times the worker count accommodates work imbalance while preventing unbounded memory growth. This preserves the strict genomic coordinate ordering required by VCF format.
Iterator Pipeline: Within each worker, processing proceeds through a lazy iterator chain with progressive filtering:
- Pileup generation: Extract reads from BAM, build per-position summaries
- Calculate metrics: Depth, allele frequencies, quality scores, etc.
- Set de-novo adjacency (context-aware): Check if adjacent positions could form de-novo CpG sites
- Add methylation info: Analyze strand-specific evidence (OT/OB strands)
- Filter site type: Early filtering to reduce downstream computation
- Apply thresholds: Hard filters on depth, frequency, quality
- Add ML metrics (context-aware): Random Forest scoring using current and adjacent positions
- Propagate CpG flags (context-aware): Coordinate CpG pair decisions
- Set variant calls: Classify as variant, methylation, or error
- Calls: Final genotype and methylation calls
- Core filter: Remove overlap positions
The "context-aware" steps are processed with parameters for the pileup metrics for the current position as well as the ones before and after. This enables CpG pair coordination and de-novo CpG detection without breaking the lazy iterator chain.
flowchart TB
Segments --> Pipeline
P11 --> Channel
Channel --> Writer
Channel["Ordered Channel"]
subgraph Main
BamReader["BAM file"] --> Segments["Genome Segments"]
end
subgraph WriterThread
Writer["VCF/BED Writer"]
end
subgraph Worker[Worker Threads]
direction TB
subgraph TLS["Thread-Local"]
Readers["BAM/FASTA Readers"]
end
subgraph Pipeline["Per-Segment Iterator Pipeline"]
direction TB
P1[Generate Pileups]
P2[Calculate Metrics]
P3[Set De-novo Adjacency]
P5[Filter for CpG sites if requested]
P7[Add Threshold Filters]
P6[ML filtering]
P8["Propagate (de-novo) CpG Flags"]
P9[Set Variant Calls]
P10[Set Genotype and Methylation Calls]
P11[Filter out overlap positions]
P1 --> P2 --> P3 --> P5 --> P6 --> P7 --> P8 --> P9 --> P10 --> P11
Readers --> P1
end
end
Output Formats
Rastair's internal representation is converted to standard bioinformatics formats for downstream analysis.
VCF Conversion
Each position generates VCF records during writer thread processing:
- One primary record: Contains all passing alternative alleles (classified as
RealVariant). For CpG sites with methylation evidence but no variants, a ref-only record (REF→.) is written. - INFO fields: Include ML score, methylation beta (ratio of methylated reads to depth), depth metrics, allele frequencies, strand bias statistics, and de-novo CpG flags.
- Genotype: Estimated using a simple error model incorporating ML scores and allele frequencies.
- Filtering: Records marked
PASSor with specific filter tags (e.g.,low_depth,low_ml_score).
BED Format
Compact TSV format for methylation data. Each line represents a single position with methylation beta, depth, and pass/fail status. Best for methylation-focused downstream analyses.
Machine Learning Integration
Random Forest models disambiguate true variants from sequencing errors and methylation artifacts.
Three Separate Models: Different variant contexts require different discriminatory features:
- CpG model: C→T or G→A at canonical CpG sites
- De-novo CpG model: Variants creating new CpG sites
- Others model: Non-CpG variants
Models are bundled as one compressed file.
A default model file is bundled in the Rastair binary and loaded at startup.
Custom models for domain-specific tuning can created with rastair's built-in ml subcommand and then specified via CLI flags.
Glossary
File Formats
SAM – Sequence Alignment Map
A text-based file format that stores sequence data in a tab-delimited format. Format Specification for version 1.0. It is used to store the alignment of sequence reads to a reference genome. SAM files are used to visualize and analyze sequence data in genome browsers like IGV.
Additional keys are defined in the Optional Fields Specification.
BAM – Binary Alignment Map
A binary version of the SAM file format. It is a compressed, indexed, and binary representation of the sequence alignment data. BAM files are used to store sequence data efficiently. They can be visualized and analyzed in genome browsers like IGV.
BED – Browser Extensible Data
A tab-separated-file format that stores genomic regions as a list of intervals.
It looks like this:
chr1 11873 12227 ENSG00000223972.5 0 +
chr1 12612 12721 ENSG00000227232.5 0 -
chr1 13220 14409 ENSG00000278267.1 0 +
The first three columns represent the chromosome, start position, and end position of the interval. The other columns contain additional information about the interval. Importantly, the start position in a bed file is 0-based, and the end position refers to the first base that is outside the interval. So, to refer to the first base of chromosome 1, one would write
chr1 0 1 Interval_of_length_1
VCF – Variant Call Format
Tab-separated-file format that stores information about genetic variants. Format Specification for VCFv4.5. It is used to represent SNPs, insertions, deletions, and other types of genetic variations. VCF files contain information about the variant's position, reference allele, alternative allele, quality score, and other annotations. @vcfPaper
It looks like this:
#CHROM POS ID REF ALT QUAL FILTER INFO FORMAT sample1 sample2
chr1 10001 . A C 30 PASS . GT:DP 0/1:10 1/1:20
chr1 10002 . T G 20 PASS . GT:DP 0/1:15 1/1:25
The first row contains the column headers. The first eight columns are mandatory fields that describe the variant. The remaining columns contain information about the samples and their genotypes. Importantly, unlike in BED, the position column in VCF files is 1-based.
FASTQ
A text-based file format that stores DNA or RNA sequences, optionally with corresponding quality scores such as produced by most sequencing machines. It is used to store raw sequencing data from high-throughput sequencing experiments. FASTQ files contain the sequence data in the form of nucleotide bases (A, T, C, G) and Phred-scaled quality scores that represent the confidence in each base call.
BCF – Binary Call Format
A binary version of the VCF file format. It stores variant calls in a compressed and indexed binary format. BCF files are more efficient for storing large variant datasets and can be used with tools like BCFtools.
BGZF – Blocked GNU Zip Format
A block compression format in which the input file is compressed as a series of GZIP-compressed blocks that can be indexed for efficient random access.
qname – query template name
A unique identifier for a sequence read in a SAM or BAM file. It is used to track the origin of the read and link it to other information in the file. Example: NB502094:69:HN2H2BGX5:2:21111:24699:8526
Genetics
TAPS – TET-Assisted Pyridine-Borane Sequencing
A method for detecting DNA modifications, such as methylation, at single-base resolution. TAPS uses a chemical reaction to convert 5-methylcytosine (5mC) to thymine (T) while leaving unmodified cytosines unchanged. Allows the detection of 5mC sites using standard sequencing technologies. Alternative to bisulfite sequencing, which can introduce biases and artifacts during the conversion process. You can read more about it here.
5Base – Illumina 5-Base sequencing
Illumina launched a chemistry that uses a custom enzyme to convert methylated (and hydroxymethylated) cytosine to thymine. The resulting data look very similar to TAPS data. Read more here.
bisulfite
A chemical treatment that converts only unmethylated cytosines to uracil in DNA. Used in bisulfite sequencing to detect DNA methylation patterns.
variant
A genomic locus that differs from the given reference genome. Variants can be SNVs, insertions, deletions, or structural changes.
allele
In cells with more than one homologous chromosomes, an allele refers to each of the observed sequences. In particular, a diploid genome will have two alleles per autosomal position.
reference allele
allele that matches the reference genome at a specific locus. Opposite to alternative allele.
alternative allele
allele that is different from the reference allele at a specific locus. Opposite to reference allele.
reference genome
Sequence of the species' genome that is used as a reference for comparing and analyzing genetic data. In particular, most alignment algorithms will use a reference genome to map reads to.
haplotype
A haplotype is a set of variants that co-occur on the same chromosome sequence, and are therefore linked.
methylation
Cytosine methylation is the enzymatic addition of a methyl group to cytosine by DNA methyltransferases. In animals, DNA methylation occurs at CpG dinucleotides.
methylated
Refers to a base that has undergone methylation.
SNV – Single Nucleotide Variant
A variation in a single nucleotide that occurs at a specific position in the genome. SNV is commonly used to refer to somatic variation, ie. a difference between eg. a cancer and its host.
SNP – Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
Formally, a SNP is a variant that occurs at a given minimum frequency in the population. However, it is nowadays often used to refer to any inherited variant in an individual.
locus
A specific position on a chromosome, for example the position of a variant in the genome.
assay
A test or procedure used to measure a specific property or characteristic of a sample. In genetics, assays are used to detect and measure genetic variations, gene expression levels, protein interactions, and other biological processes.
GIAB – Genome In a Bottle
"A public-private-academic consortium hosted by NIST to develop the technical infrastructure (reference standards, reference methods, and reference data) to enable translation of whole human genome sequencing to clinical practice and innovations in technologies." -- nist.gov
diploid genome
Genome that contains two sets of chromosome:pl, one set inherited from each parent.
indel – insertion/deletion
Variation in the genome where a small number of nucleotides are inserted or deleted.
CpG – Cytosine-phosphate-Guanine
A site in the DNA sequence where a cytosine nucleotide is followed by a guanine nucleotide in the linear sequence of bases along its 5' → 3' direction. CpG sites are often associated with gene regulation through DNA methylation.
VAF – Variant Allele Frequency
The proportion of observations of a specific alternative allele in a sample, compared to the total number of observations locus:
de-novo CpG
A CpG site that is not present in the reference genome but seems to occur in the sample when there is a variant that turns a NG (or a CN) into a CG.
Programming
Rust
A systems programming language, known for its safety, speed, and concurrency. @rustPaper
CLI – Command Line Interface
Terminal-based interface for interacting with software using text commands.
LLVM
Compiler infrastructure project, used as backend for various programming languages including the official Rust compiler.
closure
A function that "closes over" bindings in the surrounding scope, i.e., variables from around its definition location are accessible inside of it.
flamegraph
A visualization of profiled software, allowing the user to see which functions are consuming the most time. The x-axis represents the stack depth, and the y-axis represents the function name. The width of each box represents the amount of time spent in that function. @gregg2016flame
LTO – Link Time Optimization
A compiler optimization technique that performs optimizations across the entire program at link time, rather than at compile time. This can lead to improved performance and reduced code size.
CI – Continuous Integration
A software development practice where automated tests and builds are run on a regular basis (e.g. on every push to the repository) to ensure that code changes do not introduce new bugs or issues.
PGO – Profile-Guided Optimization
A compiler optimization technique that uses profiling information from previous runs of the program to optimize the code for better performance. This can lead to improved runtime performance and reduced code size.
Sequence Analysis
CIGAR – Compact Idiosyncratic Gapped Alignment Report
A string that represents the alignment of a sequence read to a reference genome. It encodes information about the alignment, including matches, mismatches, insertions, deletions, and skips. It is used in the SAM and BAM file formats.
mapQ – mapping quality
A Phred-scaled probability that the mapping position of a read is incorrect. A higher mapping quality indicates a more reliable alignment. Numbers are typically between 0 and 60.
baseQ – base quality
A Phred-scaled probability that the base call is incorrect. A higher base quality indicates a more reliable base call. Numbers are typically between 0 and 40.
OT – Original Top
The "original top" of the DNA fragment that was sequenced. The "top" by definition is the sequence that matches the reference sequence.
OB – Original Bottom
The "original bottom" of the DNA fragment that was sequenced.
record
Alternative term for read.
read – sequence read
A sequence of DNA or RNA that is generated by a high-throughput sequencing technology. In "short-read sequencing", they are typically between a few dozen and a few hundred base pairs long.
alignment
Represents the position and base-to-base mapping of a sequence read to a reference genome.
pileup
A summary of the read alignments at a specific position in the reference genome in BAM and SAM files. As a data structure, a pileup is a matrix where each row represents a read and each column represents a position in the reference genome. From this, the most likely base at that position can be inferred and used to call variants.
Statistics
RMS – Root Mean Square
Statistical measure of the average deviation of a set of values from their mean.
Chi-square test
Determine whether there is a significant association between the observed frequencies of the variables with the expected frequencies to assess the independence of the variables.
The test statistic is calculated as the sum of the squared differences between the observed and expected frequencies, divided by the expected frequencies. The resulting value is compared to a critical value from the Chi-square distribution to determine statistical significance: where is the observed frequency, is the expected frequency, and the sum is taken over all categories.
The Chi-square test is commonly used in genetics to assess the association between genetic variants and phenotypes, as well as in population genetics to test for deviations from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, which describes the expected frequencies of genotypes in a population under certain assumptions.
RF – Random Forest
Supervised learning algorithm, used for classification and regression.
ML – Machine Learning
Algorithms that can receive input data and use statistical analysis to predict an output value within an acceptable range.
Phred-scaled
A Phred-scaled quality score is a logarithmic measure of the probability that a base call is incorrect. The formula is where is the probability of an incorrect base call. A higher Phred score indicates a more reliable base call. The name "Phred" comes from the base calling software of the same name.
maximum likelihood
A method used to estimate the parameters of a statistical model. It finds the parameter values that maximize the likelihood of the observed data. The maximum likelihood estimate is the set of parameter values that make the observed data most probable. It is a common method for fitting models to data in statistics and machine learning.
Tools
SAMtools
A suite of utilities for manipulating SAM and BAM. It can manipulate SAM and BAM files. @samPaper
BCFtools
A set of utilities for manipulating variant calls in the VCF and BCF file formats. @samtoolsPaper
BEDtools
A popular suite of utilities for manipulating genomic intervals stored in BED files.
GATK – Genome Analysis Toolkit
A software package for analyzing sequencing data with tools for variant discovery, genotyping, and other analyses.
IGV – Integrative Genomics Viewer
A tool for interactive exploration of SAM and BAM files. Also see @screenshot-igv.
BWA – Burrows-Wheeler Aligner
A sequence alignment program for mapping low-divergent sequences against a large reference genome.
Minimap2
A sequence alignment program that aligns DNA or mRNA sequences against a reference database. Often used for long-read data.
htslib
A C library for reading/writing sequencing data, used by tools like SAMtools and BCFtools to manipulate SAM, BAM, and VCF files@htslibPaper. Rastair uses the Rust bindings provided by the rust-htslib crate.
bgzip
Compression tool that produces BGZF files, commonly used to compress VCF and BAM files. Part of SAMtools.
tabix
An indexing tool for tab-delimited files, such as VCF and BED files. It creates an index file that allows for efficient random access to specific regions of the file. Part of SAMtools. Homepage